How Are Cold Products Transported?
When it comes to transporting perishable goods that require temperature control, such as food and pharmaceuticals, the logistics involved are crucial to maintaining product quality and safety. Cold products need to be kept at specific temperatures throughout the transportation process to prevent spoilage, bacterial growth, and degradation. In this article, we will explore the various methods and technologies used for transporting cold products. How are cold products transported?
1. Refrigerated Trucks and Vans
Refrigerated trucks and vans are commonly used for transporting cold products over short to medium distances. These vehicles are equipped with integrated cooling systems that can maintain specific temperature ranges depending on the requirements of the goods being transported. The cooling systems in these vehicles are typically powered by the vehicle’s engine or separate generators, ensuring a constant supply of cold air.
Refrigerated trucks and vans are designed with insulated walls, ceilings, and floors to minimize heat transfer from the external environment. The cargo area is usually divided into compartments to store different products at their respective temperature requirements. Temperature monitoring and control systems are employed to maintain the desired conditions and alert the driver or operator of any deviations.
2. Refrigerated Containers
For long-distance transportation, such as international shipping, refrigerated containers, also known as reefers, are widely used. These containers are specifically designed to maintain a controlled temperature environment throughout the journey, regardless of the external climate conditions.
Refrigerated containers are equipped with powerful cooling units that can be set to the desired temperature range. These units are either powered by the container’s own generator sets or by the power supply available at the port or on board a ship. The containers’ insulated structure helps prevent heat transfer, while efficient ventilation systems ensure proper air circulation to maintain temperature uniformity.

Refrigerated containers are commonly used for transporting large quantities of perishable goods, including fruits, vegetables, meat, dairy products, and pharmaceuticals. They are loaded onto specialized refrigerated cargo ships or stacked on intermodal railcars for long-distance transport.
3. Cold Storage Facilities
Cold storage facilities play a crucial role in the cold product supply chain. These facilities act as temporary storage points where products can be stored under controlled temperature conditions before they are transported further or distributed to their final destinations.
Cold storage facilities are designed with insulated walls and efficient cooling systems that can maintain different temperature zones to accommodate various types of perishable goods. These facilities are equipped with temperature monitoring devices, alarms, and backup power supplies to ensure the integrity of the stored products.
Temperature-controlled warehouses are often strategically located near transportation hubs, allowing for seamless transfer of goods between different modes of transportation. They provide a vital link in the cold supply chain, enabling products to be stored and preserved before being loaded onto refrigerated trucks, vans, or containers for onward transport.
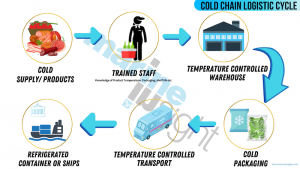
4. Cold Chain Logistics
The transportation of cold products involves a complex network of interconnected processes and stakeholders, often referred to as the cold chain logistics. Cold chain logistics is a carefully orchestrated system that ensures the integrity of perishable goods throughout the entire transportation journey.
It begins with proper packaging and loading of the products in refrigerated conditions at the point of origin. Temperature monitoring devices are used to track and record temperature data at regular intervals. This data is crucial for maintaining product quality and can serve as proof of compliance with temperature requirements during transportation.
Efficient coordination between suppliers, transporters, and receivers is vital to maintaining the cold chain. Timely deliveries, effective communication, and contingency plans for unforeseen circumstances, such as equipment failures or delays, are essential for successful cold product transportation.
Conclusion
Transporting cold products requires specialized equipment, infrastructure, and meticulous planning. Whether it’s refrigerated trucks, containers, or cold storage facilities, maintaining the required temperature throughout the journey is of utmost importance to preserve product quality and safety. The cold chain logistics system ensures that perishable goods reach their destination in optimal condition, enabling consumers to enjoy fresh and safe products. https://commgen.com.au/contact-us/
As technology continues to advance, the transportation of cold products is becoming more efficient and sustainable. Innovations such as improved insulation materials, energy-efficient cooling systems, and real-time temperature monitoring are contributing to the reliability and effectiveness of cold product transportation. By leveraging these advancements, the industry can further enhance the quality and efficiency of transporting cold products in the future.

Recent Comments