The Essential Guide to Cold Chain Transport
Understanding the Cold Chain
Transporting temperature-sensitive goods safely and effectively is a critical aspect of many industries, from pharmaceuticals and food to chemicals and biotechnology. The process of moving products while maintaining a specific temperature range is known as the “cold chain.” In this article, we will explore the concept of cold chain transport, its importance, challenges, and the key role it plays in preserving the quality and safety of various products.
What Is the Cold Chain?
The cold chain refers to the uninterrupted, temperature-controlled supply chain for products that are sensitive to temperature variations. It encompasses a series of steps involved in the storage, transportation, and distribution of products that require specific temperature conditions to ensure their quality, safety, and efficacy. These temperature-sensitive products can include perishable food items, pharmaceuticals, vaccines, blood samples, and various chemicals.
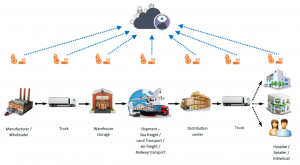
The primary goal of the cold chain is to maintain the temperature of these products within a predefined range to prevent spoilage, degradation, or loss of effectiveness. Temperature fluctuations outside of the acceptable range can result in severe consequences, including health hazards, financial losses, and reputational damage.
The Components of Cold Chain Transport
Cold chain transport involves several key components, each of which plays a crucial role in preserving the integrity of the products being transported. Let’s examine these components:
1. Temperature-Controlled Storage Facilities:
The process begins with temperature-controlled storage facilities, including warehouses and cold storage units. These facilities are equipped with specialized refrigeration and climate control systems to maintain the desired temperature and humidity levels. Temperature monitoring systems are also used to ensure that conditions remain within the specified range.
2. Refrigerated Transportation:
Transportation is a critical phase of the cold chain. Various modes of refrigerated transport, such as refrigerated trucks, containers, and air cargo, are used to move temperature-sensitive goods. These vehicles are equipped with refrigeration units and temperature monitoring devices to keep the products at the required temperature throughout the journey.
3. Packaging:
Proper packaging is essential in cold chain transport. Products are often packaged in specialized containers or insulated packaging materials that provide an extra layer of protection against temperature fluctuations. Insulated packaging helps to maintain the desired temperature, even in transit.
4. Temperature Monitoring and Data Logging:
Continuous monitoring and data logging are integral to the cold chain process. Temperature sensors and data loggers are used to track the temperature and humidity levels of the products during storage and transportation. This real-time data allows for quick response to any temperature deviations and ensures the products’ quality and safety.
5. Quality Assurance:
Quality assurance measures are implemented at each stage of the cold chain to ensure that products meet the necessary safety and quality standards. This includes regular inspections, audits, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
6. Regulatory Compliance:
Compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards is a fundamental aspect of cold chain transport. Various governing bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for pharmaceuticals and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) for perishable food items, have established guidelines that must be followed to maintain product integrity.
The Importance of Cold Chain Transport
Cold chain transport is of paramount importance in various industries due to its significant impact on product quality, safety, and public health. Let’s delve into the reasons why maintaining the cold chain is crucial:
1. Preserving Product Quality:

Many products are highly perishable and prone to spoilage when exposed to temperature variations. Cold chain transport ensures that these products maintain their intended quality and freshness. For instance, fruits and vegetables can be stored and transported at optimal temperatures to extend their shelf life.
2. Ensuring Medication Efficacy:
Pharmaceuticals and vaccines are particularly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Deviations from the recommended storage conditions can render these products ineffective or even harmful. Cold chain transport is vital for ensuring that medications maintain their intended therapeutic properties. For more information on commgen see here.
3. Food Safety:
Maintaining the cold chain is essential in the food industry to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and pathogens. Temperature-controlled transport helps reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensures that consumers receive safe and high-quality food products.
4. Reducing Economic Losses:
Failure to maintain the cold chain can result in significant economic losses. Spoiled products, especially in bulk shipments, can lead to financial setbacks for both producers and distributors. Cold chain management minimizes these losses by preserving the value of the products.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Adhering to cold chain requirements is crucial to meet regulatory standards and maintain the reputation of businesses. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues, product recalls, and damage to a company’s image.
6. Public Health and Safety:
In the case of healthcare products like blood samples and vaccines, maintaining the cold chain is a matter of public health and safety. Ensuring that these products remain effective and uncontaminated is essential for safeguarding the health of individuals.
Challenges in Cold Chain Transport
While the cold chain is vital for many industries, it comes with its set of challenges and complexities. Here are some of the key challenges faced in cold chain transport:
1. Temperature Variability:
External factors, such as weather conditions and transportation delays, can lead to temperature fluctuations. Maintaining the desired temperature range throughout the entire supply chain can be a significant challenge.
2. Equipment Failure:
Refrigeration units and temperature monitoring equipment can malfunction, jeopardizing the integrity of the products being transported. Regular maintenance and backup systems are essential to mitigate this risk.
3. Human Error:
Mistakes made by personnel at any stage of the supply chain can lead to temperature excursions. Proper training and adherence to protocols are essential to minimize human error.
4. Infrastructure Limitations:
In some regions, limited access to temperature-controlled storage and transportation infrastructure can hinder cold chain logistics. This is especially challenging in developing countries.
5. Cost:
Maintaining the cold chain requires substantial investment in equipment, technology, and personnel. This cost can be a barrier for smaller businesses and less developed regions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cold chain transport is a critical component of various industries, ensuring the safe and efficient movement of temperature-sensitive products. From preserving product quality and safety to complying with regulatory standards, the importance of the cold chain cannot be overstated. While it presents challenges, advancements in technology and best practices continue to improve the reliability and efficiency of cold chain management. As industries continue to grow and evolve, cold chain transport will remain an indispensable part of their operations, safeguarding product quality and public health.

Recent Comments