What Are the Components of a Cold Room?
When it comes to storing perishable goods, maintaining the ideal temperature is crucial to prevent spoilage and ensure product quality. Cold rooms are specially designed storage spaces that provide the necessary cooling environment for various industries, including food and pharmaceuticals. A cold room consists of several components working together to create and maintain low temperatures. In this article, we will explore the essential components of a cold room and their functions.
1. Insulated Panels
The foundation of a cold room is its insulated panels. These panels are typically made of high-quality materials such as polyurethane foam or polystyrene, which offer excellent thermal insulation properties. The panels are designed to minimize heat transfer between the inside and outside environments, effectively preserving the desired low temperature inside the cold room.
The insulation provided by these panels helps reduce energy consumption by preventing heat infiltration. The thickness and density of the insulation material are carefully chosen based on the required temperature range and the specific needs of the stored products.
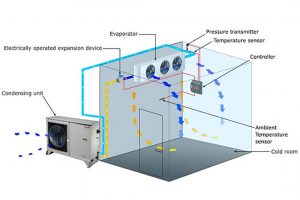
2. Refrigeration System
The refrigeration system is the heart of a cold room, responsible for maintaining the desired temperature. It consists of various components that work together to remove heat from the cold room and keep the interior cool. The key components of a typical refrigeration system include:
a. Compressor
The compressor is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure, and increasing its temperature. This high-pressure gas then moves to the condenser.
b. Condenser
In the condenser, the high-pressure refrigerant gas is cooled down and condensed into a high-pressure liquid. Heat from the refrigerant is released to the surrounding environment, usually with the help of a fan or water cooling system.
c. Expansion Valve
Once the refrigerant has been condensed, it passes through the expansion valve. This valve regulates the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator and reduces its pressure, causing it to evaporate.
d. Evaporator
The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the cold room, thus cooling down the interior. As the low-pressure refrigerant evaporates, it draws heat from the surroundings, including the stored products. The resulting gas is then drawn back into the compressor to restart the refrigeration cycle.
3. Temperature Control System
To maintain the desired temperature range inside the cold room, a reliable temperature control system is essential. This system comprises sensors, controllers, and actuators that monitor and regulate the temperature, ensuring it remains within the specified limits.
Sensors placed strategically throughout the cold room constantly measure the temperature and send signals to the controller. The controller analyzes the temperature data and activates the necessary components, such as the compressor or fans, to adjust the cooling output accordingly. This continuous monitoring and adjustment ensure that the cold room maintains a stable temperature, protecting the integrity of the stored products.
Modern cold room temperature control systems often come with advanced features, such as remote monitoring and alert systems. These allow facility managers to monitor the cold room’s temperature and receive real-time notifications if any deviations occur. Such systems help prevent product spoilage and enable timely corrective actions to be taken.
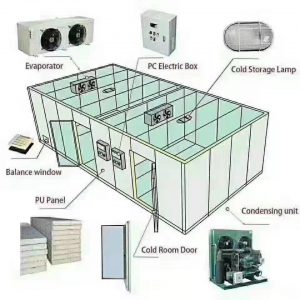
Conclusion
Cold rooms are critical for industries that require controlled environments to store perishable goods. The components mentioned above work together to create and maintain low temperatures, ensuring that products remain fresh and of high quality. The insulated panels provide thermal insulation, while the refrigeration system cools down the interior, and the temperature control system ensures precise temperature regulation.
When designing or operating a cold room, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the stored products and the desired temperature range. This includes factors such as insulation thickness, refrigeration capacity, and temperature control accuracy. Proper maintenance of the components is also crucial to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
In addition to the essential components mentioned above, cold rooms may also incorporate other features to enhance functionality and convenience. These can include:
1. Doors and Sealing Systems
Cold room doors are designed to provide a tight seal to prevent warm air from entering and cold air from escaping. They are often equipped with gaskets or magnetic strips to ensure an airtight closure. Some advanced cold rooms may also have automated door systems that open and close quickly to minimize temperature fluctuations during access.
2. Shelving and Racking
To maximize storage space and organization, cold rooms can be equipped with shelving and racking systems. These provide efficient utilization of the available space and facilitate easy access to the stored products. It is important to choose shelving and racking materials that are resistant to low temperatures and corrosion. https://commgen.com.au/about-us/
3. Lighting
Proper lighting is necessary for visibility and safety within the cold room. LED lighting is often preferred due to its energy efficiency and resistance to low temperatures. It is important to choose lighting fixtures that are designed specifically for cold room applications to ensure reliable performance.
4. Alarm Systems
To further enhance product safety and security, cold rooms may be equipped with alarm systems. These systems can detect temperature deviations, power failures, or other critical events and trigger audible or visual alerts. Alarm systems help ensure timely response to potential issues, minimizing the risk of product loss.
In conclusion, a cold room is a sophisticated storage solution that relies on several key components to create and maintain the ideal temperature for perishable goods. Insulated panels, refrigeration systems, and temperature control systems form the foundation of a cold room, while additional features such as doors, shelving, lighting, and alarm systems contribute to its functionality and efficiency. By understanding the components and their roles, businesses can optimize the performance of their cold rooms, ensuring the preservation of product quality and extending shelf life.

Recent Comments