How IoT and Sensors Are Transforming Cold Storage Temperature Control
Cold storage facilities are under increasing pressure to maintain precise temperature conditions while reducing operational costs, meeting strict regulatory requirements, and minimizing product loss. Traditional temperature control methods, which often rely on manual monitoring and reactive maintenance, are no longer sufficient for modern cold storage operations. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology and advanced sensors is fundamentally transforming how temperature control is managed in cold storage environments.
By enabling real-time monitoring, automation, predictive analytics, and remote management, IoT and sensor-based systems are redefining temperature control standards across food, pharmaceutical, and logistics cold chains.
The Role of Temperature Control in Cold Storage Operations
Temperature control is critical to preserving product quality, safety, and shelf life. Even small deviations can result in spoilage, reduced efficacy of pharmaceuticals, or regulatory non-compliance.
Challenges of Traditional Temperature Monitoring
Conventional cold storage temperature control often involves:
Manual temperature checks at fixed intervals
Limited sensor coverage
Delayed response to temperature deviations
Minimal historical data for analysis
These limitations increase the risk of undetected temperature fluctuations and make it difficult to identify root causes of inefficiencies or failures.
What Is IoT in Cold Storage Temperature Control?
IoT refers to a network of connected devices that collect, transmit, and analyze data in real time. In cold storage facilities, IoT systems connect temperature sensors, refrigeration equipment, control units, and software platforms into a unified ecosystem.
How IoT Systems Function
IoT-enabled cold storage systems continuously gather temperature data from sensors placed throughout storage rooms. This data is transmitted to centralized platforms where it is analyzed and used to automatically adjust cooling systems or trigger alerts when conditions fall outside acceptable ranges.
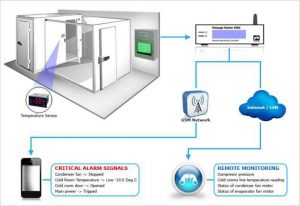
The Importance of Sensors in Cold Storage Environments
Sensors are the foundation of IoT-driven temperature control. Their accuracy and placement directly influence system performance.
Types of Sensors Used in Cold Storage
Modern cold storage facilities utilize several sensor types, including:
High-precision digital temperature sensors
Humidity sensors
Door status sensors
Airflow and pressure sensors
Together, these sensors provide a complete picture of environmental conditions within cold storage rooms.
Strategic Sensor Placement
Sensors are placed in critical zones such as near doors, evaporators, high-traffic areas, and product hotspots. This eliminates blind spots and ensures temperature uniformity across the storage space.
Real-Time Temperature Monitoring and Visibility
One of the most significant benefits of IoT and sensor technology is real-time visibility into cold storage conditions.
Continuous Data Collection
Unlike periodic manual checks, IoT sensors collect data continuously. This allows operators to detect even minor temperature fluctuations immediately, reducing the risk of prolonged exposure to unsafe conditions.
Remote Access and Dashboards
Cloud-based dashboards allow facility managers to monitor temperatures, system performance, and alarms remotely. This is especially valuable for multi-site operations and after-hours monitoring.
Automation and Intelligent Temperature Control
IoT-enabled systems go beyond monitoring by actively controlling temperature conditions.
Automated System Adjustments
When sensors detect temperature changes, IoT systems can automatically adjust compressor output, fan speed, or defrost cycles. This proactive approach maintains stable temperatures without manual intervention.
Adaptive and Self-Learning Controls
Advanced systems analyze historical data and operational patterns, such as door openings or product loading schedules. Over time, they optimize temperature control strategies to improve performance and efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Energy consumption is one of the largest operating expenses in cold storage facilities. IoT and sensors play a key role in reducing these costs.
Optimized Refrigeration Performance
Real-time sensor data enables systems to deliver cooling only when and where it is needed. This reduces unnecessary runtime, minimizes equipment strain, and lowers electricity consumption.
Identifying Inefficiencies
Analytics platforms highlight trends such as excessive cycling, temperature instability, or poor insulation performance. Addressing these issues leads to measurable energy savings.
Predictive Maintenance and Equipment Reliability
Unexpected equipment failure can be costly and disruptive. IoT-driven predictive maintenance helps prevent these issues.
Early Fault Detection
Sensors monitor performance indicators such as temperature recovery time and system response. Deviations from normal patterns can signal emerging problems before failure occurs.
Reduced Downtime and Maintenance Costs
By scheduling maintenance based on actual equipment condition rather than fixed intervals, facilities reduce downtime, extend equipment lifespan, and lower repair costs.
Compliance, Traceability, and Data Integrity
Cold storage facilities must comply with strict regulatory requirements, particularly in food and pharmaceutical industries.
Automated Temperature Logging
IoT systems automatically record temperature data, creating accurate and tamper-proof logs. This simplifies audits and inspections while reducing administrative workload.
Improved Traceability
Historical data allows operators to trace temperature conditions for specific batches or time periods, supporting quality assurance and customer confidence.
Scalability and Multi-Site Management
IoT-based temperature control systems are highly scalable, making them ideal for growing operations.
Centralized Control Across Facilities
Multiple cold storage rooms or sites can be managed from a single platform. Standardized monitoring and control improve consistency and operational efficiency.
Future-Proof Infrastructure
IoT systems can be expanded with additional sensors, integrations, and analytics tools as operational needs evolve.
The Future of IoT and Sensors in Cold Storage
The role of IoT and sensors in cold storage will continue to expand as technology advances.
Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Analytics
AI-powered systems will further enhance decision-making by predicting temperature risks, optimizing energy use, and adapting to changing operational demands.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Improved energy efficiency and reduced waste contribute to sustainability goals, helping cold storage operators reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining high performance.
Conclusion
IoT and sensor technology are transforming cold storage temperature control from a reactive process into an intelligent, data-driven operation. Through real-time monitoring, automation, predictive maintenance, and advanced analytics, these systems deliver greater accuracy, efficiency, and reliability.
As cold storage requirements become more complex and regulatory expectations rise, adopting IoT-enabled temperature control is no longer a competitive advantage—it is a necessity. Facilities that embrace these technologies are better positioned to protect product quality, reduce costs, and ensure long-term operational success.

Recent Comments